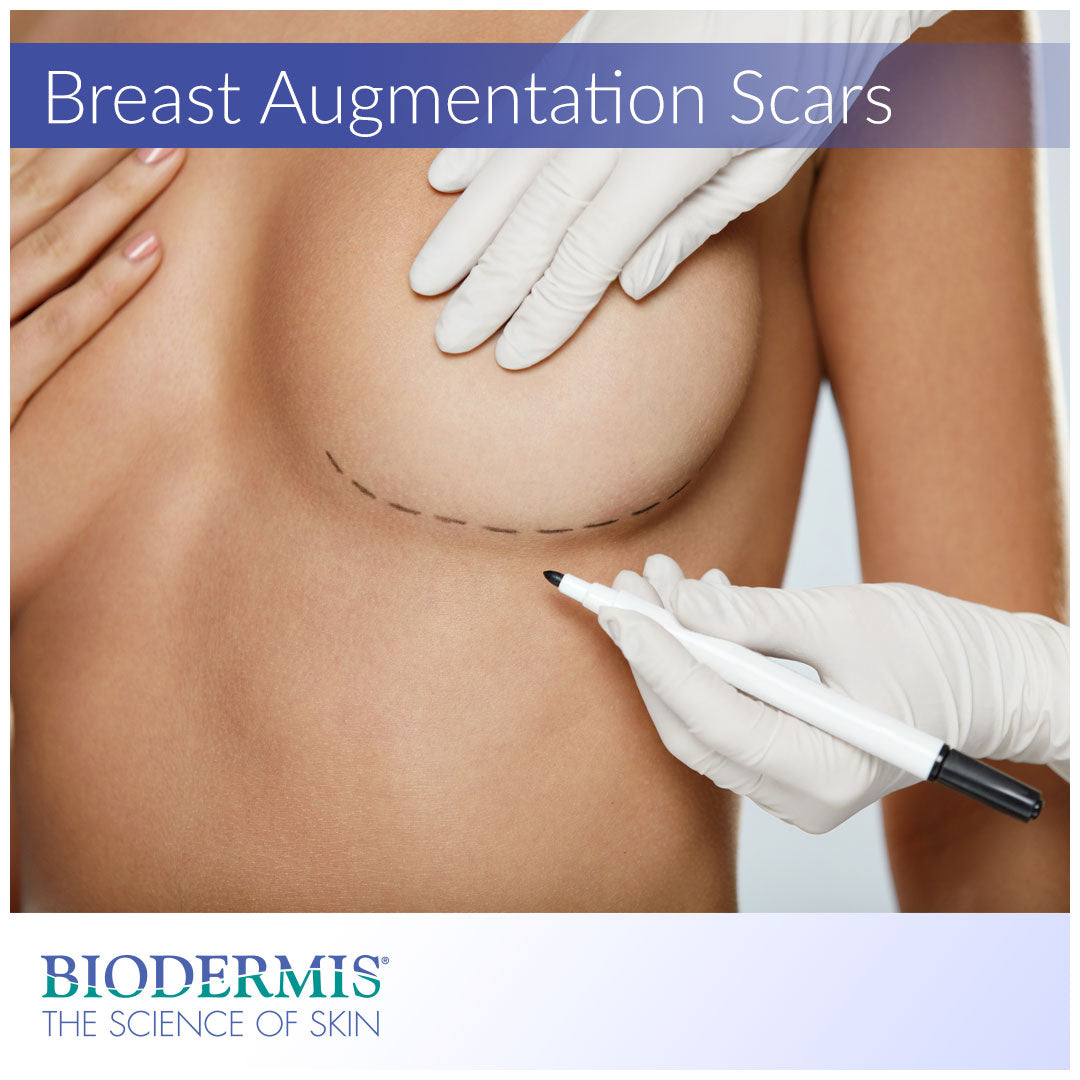
Continue reading to learn more about breast augmentation procedures and to discover clinically-proven ways to prevent and reduce significant post-surgical scarring.
Breast augmentation incision techniques
Plastic surgeons employ a number of breast enhancement techniques that address each patient’s unique anatomy, breast profile, and desired shape. Through the use of breast implants and different incision types, a number of modifications can be made to breasts of all shapes and sizes. Depending on the incision method utilized, and the patient’s ideal post-surgical results, amount of scarring and recovery time can vary. Listed below are a few incision techniques involved in augmentation procedures and how they allow the surgeon to contour the shape and size of the breast.
Listed below is your guide to understanding different mammoplasty techniques and the extent of what each can achieve for your ideal silhouette.


Periareolar incisions are made along the outer perimeter of the lower areola in the shape of a semicircle. Because areola tissue differs in complexion from the surrounding skin, scars resulting from this incision blend in quite nicely. Similar to inframammary incisions, the surgeon will create a pocket above or below the pectoral muscle to situate the implant. Because the point of incision is small and proximate to the implant site, plastic surgeons can more easily control blood loss and exercise surgical precision. The unfortunate drawback to this procedure concerns patients who are prone tohypertrophic or keloid scarring. If the post-augmentation wound doesn’t heal well, which can happen regardless of surgical expertise, scarring will be clearly noticeable.

Transaxillary incisions are made in the armpit (axilla) region. Transaxillary incisions are small, about 1 to 2 inches in length, along a natural crease in the armpit. Once the incision is made, the plastic surgeon will develop a subcutaneous channel from the access point to underneath the breast where the implant will be situated. Subpectoral and subglandular implant placements can be performed similar to other augmentation techniques. Transaxillary procedures are an attractive option for patients who wish to avoid scarring on the areola or breast area. Another advantage of this incision is that it reduces the risk of nerve damage in the nipple, which can impact nipple sensitivity. Not all plastic surgeons offer this type of augmentation procedure as it requires greater surgical expertise compared to other styles.
Post-operative recovery and scar management
For the best cosmetic results after your breast augmentation surgery, it’s important to follow the specific instructions of your surgeon. Generally, patients are cleared to return home after roughly one hour following surgery. Compression garments or support bras may be worn to promote rapid recovery and uniform healing. Some doctors will prescribe pain medication to abate discomfort from post-operative swelling and bruising. Patients should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise for several weeks or until further instructed by their surgeons.
Any form of invasive surgical procedure will leave scarring, and some patients will scar more than others. Scarring is influenced by a number of factors including genetics, skin type, and how well one manages their scar. To prevent and reduce significant scarring post-surgery,silicone gel sheeting should be worn.

Silicone gel technology emerged over 30 years ago as a safe and effective topical solution for scars, and numerous clinical studies substantiate this claim. Through the mechanisms of hydration and collagen regulation, medical silicone gives the user control over scar formation. Silicone is an effective treatment solution for scars resulting from injury and surgical procedures. Silicone sheeting designed specifically for breast augmentation procedures can be easily obtained online at biodermis.com.
Biodermis is an innovative market leader with 30 years of expertise in the medical silicone industry. Visit Biodermis.com today to explore a complete range of scar management and post-operative care solutions.
Biodermis offers custom tailored referral programs designed to simplify and reduce the cost of your patients' post-op care. Additionally, we offer professional pricing if you opt to retail our products. Give us a call at 800.322.3729, and we will be happy to provide additional details on these programs.